概述 疑问1 为什么某些程序位于 /bin 下,或者 /sbin ,或者 /usr/bin ,或 /usr/sbin 目录下吗?例如, less 命令位于 /usr/bin 目录下。为什么没在 /bin 中,或 /sbin ,或 /usr/sbin 目录中?所有这些目录之间有什么不同?
疑问2 为什么很多发行版本,比如 Centos 、 Red hat 、 SuSE 。它们的 / (根)目录下都有相同的目录结构?比如 /etc 、 /home 、 /dev 、 /var 、 /tmp 。为什么叫这些名字,这些目录下放的都是什么东西?
文件系统目录标准 由于 Linux 家喻户晓,开发人员众多,目录也越来越多,如果没有一个统一的标准,那么不同的发行版文件放置位置也不同,相同文件的名称也不同,这样看起来会非常的杂乱无章,在这种情况下 FHS 的出现就是必然的了。
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard(文件系统目录标准)的缩写,多数 Linux 版本采用这种文件组织形式,类似于 Windows 操作系统中 c 盘的文件目录, FHS 采用树形结构组织文件。 FHS 定义了系统中每个区域的用途、所需要的最小构成的文件和目录,同时还给出了例外处理与矛盾处理。
FHS 定义了两层规范,第一层是 / 目录下要放置哪些文件数据。第二层则是针对 /usr 和 /var 这两个目录的子目录定义。
目录说明 目录特点
/(根)是所有目录的顶点。目录结构像一颗倒挂的树。
目录和磁盘分区,默认是没有关联的。
/(根)下不同的目录可能会对应不同的分区或磁盘。所有的目录都是按照一定的类别和规律组成的。
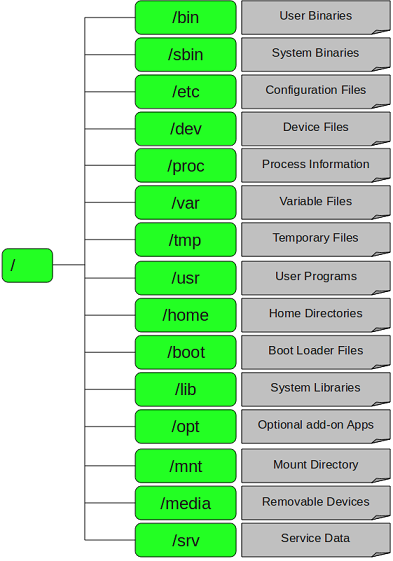
目录结构 FHS规定的 / (根)目录下各目录结构,如下图
目录说明 / (根)目录 每一个文件和目录从根开始,/ 下的目录有
script 1 2 3 [root@centos /]# ls bin data etc lib lost+found mnt opt root selinux sys usr boot dev home lib64 media daxin proc sbin srv tmp var
/bin 目录 用来存放二进制可执行命令的目录,用户常用的命令都存在该目录下。例如:mkdir(创建目录)、cat(查看文件)、find(查找文件)等。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [root@centos bin]# ls alsaunmute egrep mkdir sh arch env mknod sleep awk ex mktemp sort basename false more stty bash fgrep mount su cat find mountpoint sync chgrp findmnt mv tar …… [root@centos bin]#
/sbin 目录 同样用来存放二进制可执行文件,只是这里面的命令只供系统管理员,管理系统使用(root用户)。例如:iptables(防护墙)、ifconfig(查看网卡信息)、init(设置启动级别)等。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@centos sbin]# ls accton ip partx addpart ip6tables pccardctl agetty ip6tables-1.4.7 pidof …… init nologin vgscan initctl pam_console_apply vgsplit insmod pam_tally2 vmcore-dmesg insmod.static pam_timestamp_check weak-modules install-info parted wipefs installkernel partprobe [root@centos sbin]#
/dev 目录 设备文件存放的目录,因为linux中一切皆文件,所以就像鼠标、键盘、光驱,对linux来说也都是一个个的文件。例如/dev/cdrom(光驱)、/dev/sda1(硬盘)等。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [root@centos dev]# ls agpgart lp0 rfkill tty24 tty57 block lp1 root tty25 tty58 bsg lp2 rtc tty26 tty59 btrfs-control lp3 rtc0 tty27 tty6 bus MAKEDEV scd0 tty28 tty60 …… loop5 ram9 tty21 tty54 vga_arbiter loop6 random tty22 tty55 zero loop7 raw tty23 tty56 [root@centos dev]#
/tmp 临时文件存放的地方,由于这个目录的权限为 777,所有用户对这个目录都有可读可写可执行的权限,所以其他人也可以删除你的文件。(可以当作windows的回收站来用,不用的东西先放这里)。
script 1 2 3 [root@centos tmp]# ls 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt 4 5 6 [root@centos tmp]#
/home 普通用户的家目录,用来存放普通用户的文件。比如我们新建一个用户(useradd)会在/home下创建和这个用户同名的家目录。
script 1 2 3 4 5 [root@centos home]# ls -l total 4 drwx------. 3 lzy lzy 4096 Oct 31 13:05 lzy [root@centos home]# # 说明我们系统中有一个用户名字是lzy,他的家目录在/home/lzy。
/boot目录 存放内核文件和系统引导程序
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [root@centos boot]# ls config-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 efi grub initramfs-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.img lost+found symvers-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.gz System.map-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 vmlinuz-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 [root@centos boot]#
/lib目录 存放二进制库文件,库文件一般以.so|lib|ld 。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [root@centos lib]# ls alsa libnsl.so.1 cpp libnss_compat-2.12.so crda libnss_compat.so.2 firmware libnss_dns-2.12.so i686 libnss_dns.so.2 … [root@centos lib]#
/mnt目录 一般用来临时挂载临时存储设备的目录
script 1 2 [root@centos /]# ls -ld /mnt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Sep 23 2011 /mnt
/opt目录 该目录是可选的,一般是给第三方厂家开发的程序的安装目录。现在一般不用了。
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos /]# cd /opt [root@centos opt]# ls rh [root@centos opt]#
用于挂载可移动设备的临时目录。
script 1 2 3 [root@centos /]# ls -ld /mnt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Sep 23 2011 /mnt [root@centos /]#
/root目录 系统管理员的家目录。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 [root@centos ~]# ls -a . .bash_logout install.log .tcshrc .. .bash_profile install.log.syslog .viminfo anaconda-ks.cfg .bashrc ipaddress .bash_history .cshrc .lesshst [root@centos ~]#
/sys目录 与/proc一样,存放系统运行过程中的信息文件。
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos sys]# ls block class devices fs kernel power bus dev firmware hypervisor module [root@centos sys]#
/etc目录 yum/rpm安装的软件配置文件所在的目录。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [root@centos etc]# ls abrt mtab acpi my.cnf adjtime nanorc …… mime.types xinetd.d mke2fs.conf xml modprobe.d yum modulefiles yum.conf motd yum.repos.d [root@centos etc]#
/usr目录 安装除操作系统本身外的一些应用程序或组件的目录,一般可以认为是linux系统上安装的应用程序默认都安装在此目录中;
script 1 2 3 4 5 [root@centos etc]# cd /usr [root@centos usr]# ls bin games lib libexec sbin src etc include lib64 local share tmp [root@centos usr]#
特殊文件说明 网卡配置文件 文件位置为:/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 ,该文件控制网卡的配置信息,网卡的配置文件统一放在 network-scripts 中,eth1 表示第二块网卡,依次累加。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@centos usr]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 #设备名称 TYPE=Ethernet #设备类型为Ethernet ONBOOT=yes #开机启动 NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=none #IP获取方式 IPADDR=10.0.0.8 #IP地址 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 #网络掩码 DNS2=4.4.4.4 #备用DNS地址 GATEWAY=10.0.0.2 #网关地址 DNS1=10.0.0.2 #主用DNS地址 [root@centos usr]#
特殊字段说明:
NM_CONTROLLED表示是否启用NetworkManager管理,NetworkManager是一个图形管理工具,没有装图形界面该选项可以改为no。
BOOTPROTO 表示获取IP的方式,动态获取(dhcp),静态配置(static),无(none)。
DNS解析配置文件 文件位置为:/etc/resolv.conf,该文件用来指定DNS服务器地址(DNS:网络地址解析)
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos tmp]# more /etc/resolv.conf nameserver 10.0.0.2 #DNS服务器地址 nameserver 4.4.4.4
设置DNS方式:
直接编辑 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 [root@centos7 ~]#cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=eth0 UUID=8a8ffc84-3b73-4da3-9562-6101037ad60d DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes # 开机启动 IPADDR=10.0.0.13 # IP地址 PREFIX=24 # 掩码前缀 GATEWAY=10.0.0.2 # 网关 DNS1=223.5.5.5 # 添加DNS1配置 IPV6_PRIVACY=no
或:
script 1 echo 'DNS=4.4.4.4' >> /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
注意:
修改完DNS、IP之后需要重启网络生效。
/etc/init.d/network restart
Service network restart
Ifdown eth0 && ifup eth0 (重启网卡)
ifcfg-eth0的配置文件优先级高于/etc/resolv.conf文件。
系统默认会从/etc/resolv.conf中读取DNS地址,可以直接更改该文件达到临时修改的目的。
局域网DNS解析文件 文件位置为:/etc/hosts,一般用来进行局域网DNS重定向。
script 1 2 3 4 5 [root@centos tmp]# cat /etc/hosts cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.1.1 www.baidu.com #IP地址 域名
注意:
主机名配置文件 文件位置为:/etc/sysconfig/network
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos tmp]# more /etc/sysconfig/network NETWORKING=yes #是否启用网络 HOSTNAME=centos #主机名 [root@centos tmp]#
设置方法:
hostname hostname(临时设置主机名)
sed -i ‘s@HOSTNAME=centos@HOSTNAME=XXX@g’ /etc/sysconfig/network (永久更改,需要重启,一般搭配hostname使用)
开机自动挂载文件系统配置文件 文件位置为:/etc/fstab,主要存放开机自动挂载信息.
各段说明:
第一段,表示文件系统的名称(或者UUID,系统唯一识别码),Blkid 可以查看。
第二段,表示文件系统的挂载点。
第三段,表示文件系统的类型。
第四段,表示挂载文件系统时的属性。
第五段,第一列表示是否进行dump备份,第二列表示开机是否对磁盘进行fsck检查。
小技巧:
当有一些外置磁盘需要开机挂载的时候,我们可以把该磁盘信息添加到该文件中,但要注意的是,如果这块外置磁盘在开机的时候报错,那我们整个系统就起不来了,所以要慎用,如果确实需要开机挂载,可以在/etc/rc.local中写入挂载命令即可。
启动命令存放文件 文件位置:/etc/rc.local
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 [root@centos etc]# more rc.local # !/bin/sh # # This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts. # You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't # want to do the full Sys V style init stuff. touch /var/lock/subsys/local [root@centos etc]#
注释:
该文件是一个软连接文件,链接到 /etc/rc.d/rc.local 文件中。该文件是登陆shell 之前最后调用的一个文件,一般用来存放需要开机启动的软件的命令。
启动级别配置文件 文件位置:/etc/inittab
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 [root@centos rc.d]# cat /etc/inittab …… # Default runlevel. The runlevels used are: # 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this) # 1 - Single user mode # 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking) # 3 - Full multiuser mode # 4 - unused # 5 - X11 # 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this) # id:3:initdefault: [root@centos rc.d]#
启动级别说明:
0:表示关机
1:表示单用户模式
2:表示多用户模式,但没有NFS服务(NFS:网络文件系统)
3:表示完整的多用户模式(命令行模式)
4:保留不用
5:图形界面
6:表示重启
我们日常使用的界面为3,可以使用init 来设置启动级别。
启动脚本目录 文件位置:/etc/init.d/,所有服务的默认启动脚本都存放在这里,是一个链接文件,链接到 /etc/rc.d/init.d 目录。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 [root@centos etc]# ls -l init.d lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 Mar 3 23:25 init.d -> rc.d/init.d [root@centos etc]# ls init.d abrt-ccpp functions lvm2-monitor postfix saslauthd abrtd haldaemon mdmonitor psacct single abrt-oops halt messagebus quota_nld smartd acpid ip6tables netconsole rdisc sshd atd iptables netfs rdma svnserve auditd irqbalance network restorecond sysstat blk-availability kdump nfs-rdma rngd udev-post cpuspeed killall ntpd rsyslog crond lvm2-lvmetad ntpdate sandbox [root@centos etc]#
设置开机启动:
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 # 查看系统启动服务(chkconfig) [root@centos ~]# chkconfig --list crond 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off iptables 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off network 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off ntpd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off rsyslog 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off sshd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off sysstat 0:off 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off …… [root@centos ~]# # 修改某个启动服务为开机启动 [root@centos init.d]# chkconfig --level 2345 iptables on [root@centos init.d]# chkconfig --list | grep iptables iptables 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@centos init.d]# # 添加/删除某个服务到开机启动 [root@centos init.d]# chkconfig --add xiaoming [root@centos init.d]# chkconfig --del xiaoming 注意:由于chkconfig启动服务有严格的格式,所以我们需要调整启动脚本在脚本头部添加如下字段: # !/bin/sh # chkconfig 2345 99 99 # description:this is apache start script
环境变量配置文件 文件目录:/etc/profile ,用来存放用户的环境变量配置(例如umask等)在登陆shell设置环境变量的时候,该文件会调用 /etc/profile.d 目录下的文件,我们定义别名,或者其他变量的时候,可以在 /etc/profile.d 下创建文件即可。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 [root@centos ~]# ls !$ ls /etc/profile.d/ colorls.csh cvs.sh lang.csh less.sh vim.csh colorls.sh glib2.csh lang.sh modules.csh vim.sh cvs.csh glib2.sh less.csh modules.sh which2.sh [root@centos ~]#
登录之前提示信息 文件位置:/etc/issue ,主要存放的是我们还没有登陆系统的时候的提示信息。(CRT或者Xshell可能会看不到)
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos ~]# cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.7 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m [root@centos ~]#
字段说明:
第一行显示的是系统版本信息
第二行显示的是内核版本。
为了安全起见可以清空该文件,这样其他用户登陆系统之前,就不会预先获得系统的版本和内核版本信息了。
登陆之后显示的欢迎信息 文件位置:/etc/motd ,主要存放的是我们登陆系统之后的欢迎信息。
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos ~]# cat !$ (!$表示上一个命令的最后一个参数) cat /etc/motd welcome to my home [root@centos ~]#
源码包目录 文件位置:/usr/local ,一般存放用户上传的文件的目录。
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos ~]# cd /usr/local/ [root@centos local]# ls bin etc games include lib lib64 libexec sbin share src [root@centos local]#
用户上传软件的目录 文件位置:/usr/src ,一般存放自己编译的源码包的目录。
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos usr]# cd src [root@centos src]# ls debug kernels [root@centos src]#
系统日志文件 文件目录:/var/log/messages ,记录系统日志文件。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [root@centos src]# head -5 /var/log/messages Mar 7 18:50:02 Beyond rsyslogd: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="5.8.10" x-pid="1327" x-info="http://www.rsyslog.com"] rsyslogd was HUPed Mar 7 20:46:36 Beyond kernel: e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Down Mar 7 20:46:43 Beyond kernel: e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: None Mar 7 20:46:45 Beyond kernel: e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Down Mar 7 20:46:51 Beyond kernel: e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: None [root@centos src]#
注意:
/var/log/message ,是由 rsyslog 来进行写入的,所以如果查看该文件没有内容,请确认 rsyslog 进程状态是否正常。
使用dmesg命令查看系统的故障信息
系统安全日志文件 文件位置:/var/log/secure,主要存放用户验证,鉴权等信息的文件,像ssh远程登陆的信息包括验证成功,验证失败都会记录在这里。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [root@centos src]# head -5 /var/log/secure Mar 7 20:39:18 Beyond sshd[1792]: pam_unix(sshd:session): session closed for user root Mar 7 20:39:27 Beyond sshd[2358]: Address 10.0.0.1 maps to bogon, but this does not map back to the address - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT! Mar 7 20:39:27 Beyond sshd[2358]: Accepted password for root from 10.0.0.1 port 53376 ssh2 Mar 7 20:39:28 Beyond sshd[2358]: pam_unix(sshd:session): session opened for user root by (uid=0) Mar 7 20:47:52 Beyond sshd[2391]: Address 10.0.0.1 maps to bogon, but this does not map back to the address - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT! [root@centos src]#
注意:
没事查看一下该文件,因为ssh链接失败的日志会记录在这里,可以防止别人暴力破解我们的密码。
定时任务配置目录 文件位置: /var/spool/cron/ ,所有用户的 crontab 配置文件都会写入 /var/spool/cron 下,以用户名为文件中。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [root@centos spool]# cd cron/ [root@centos cron]# ls root [root@centos cron]# # Crontab,计划任务,用来周期的执行某些命令,常用来定期删除日志,或者定期执行某些脚本,由crond进程守护。使用crontab –l来查看当前用户的计划任务。 [root@centos cron]# crontab -l * * * * * echo '123' >/dev/null 2>&1 [root@centos cron]#
crontab中的分段解释
前面的5个星分别表示,分、时、日、月、周,*表示任意,所以上面的命令意思是任何时间都要执行 echo “123” >/dev/null 这条命令。
/dev/null 文件可以理解为黑洞,所有数据到这个文件中,都会消失的无影无踪。使用 crontab –e 设置计划任务,编辑完毕后输入:wq退出
script 1 2 3 4 [root@centos cron]# crontab -e * * * * * echo '123' >/dev/null 2>&1 ~ [root@centos cron]#
CPU配置信息 文件位置: /proc/cpuinfo,伪文件系统,不占用磁盘空间,主要显示cpu的配置信息
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 [root@centos cron]# cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 vendor_id : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 58 model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3630QM CPU @ 2.40GHz stepping : 9 microcode : 27 cpu MHz : 2394.566 cache size : 6144 KB physical id : 0 siblings : 1 core id : 0 cpu cores : 1 apicid : 0 initial apicid : 0 fpu : yes fpu_exception : yes cpuid level : 13 wp : yes ……
内存配置信息 文件位置:/proc/meminfo ,伪文件系统,不占用磁盘空间,主要显示内存的配置信息。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [root@centos cron]# cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 486644 kB MemFree: 390444 kB Buffers: 12532 kB Cached: 29184 kB SwapCached: 0 kB Active: 17792 kB Inactive: 29068 kB Active(anon): 5160 kB Inactive(anon): 168 kB Active(file): 12632 kB /proc/loadavg /proc/mounts ……
注意:使用 free –m(设置单位为Mb)也可以查看内存的使用情况
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 [root@centos cron]# free -m total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 475 94 381 0 12 28 -/+ buffers/cache: 53 421 Swap: 767 0 767 [root@centos cron]#
系统平均负载信息 文件位置:/proc/loadavg ,存放系统平衡负载等相关信息,比如我们使用的 uptime、top、w 命令都会显示系统的平均负载。
script 1 2 3 [root@centos cron]# cat /proc/loadavg 0.00 0.00 0.00 1/73 1633 [root@centos cron]#
注意:
各字段表示,1分钟内平均负载、5分钟内平均负载、15分钟内平均负载,1/73分子是正在运行的进程数,分母是总进程数。1633表示最近运行的进程进程号。
1分钟内平均负载,建议每个CPU不要超过3,具体计算公式为(1分钟内平均负载)/(cpu核数)❤️,超过5的话,要进行优化了。
系统挂载信息 文件目录:/proc/mounts ,显示当前系统的所有磁盘挂载信息,包括文件系统名称,挂载点,文件系统类型,挂载属性 等信息。
script 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@centos cron]# cat /proc/mounts rootfs / rootfs rw 0 0 proc /proc proc rw,relatime 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs rw,relatime 0 0 devtmpfs /dev devtmpfs rw,relatime,size=228024k,nr_inodes=57006,mode=755 0 0 devpts /dev/pts devpts rw,relatime,gid=5,mode=620,ptmxmode=000 0 0 tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs rw,relatime 0 0 /dev/sda3 / ext4 rw,relatime,barrier=1,data=ordered 0 0 /proc/bus/usb /proc/bus/usb usbfs rw,relatime 0 0 /dev/sda1 /boot ext4 rw,relatime,barrier=1,data=ordered 0 0 none /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc binfmt_misc rw,relatime 0 0 [root@centos cron]#